Imminent migraines have several signs, including problems with sleep, concentration, and vision. When these unwelcome surprises occur, you likely focus on dealing with the pain as best you can until it’s over. However, to prevent future migraines, it’s essential to determine possible triggers. Doing so may reduce how often they occur.
Of course, not all triggers are external. Some neurological conditions, including Multiple Sclerosis, epilepsy, or fibromyalgia, can cause migraines or similar headache pain. Your doctor may offer treatment options for these issues. For more information on migraines caused by sounds, smells, and other sources, keep reading.
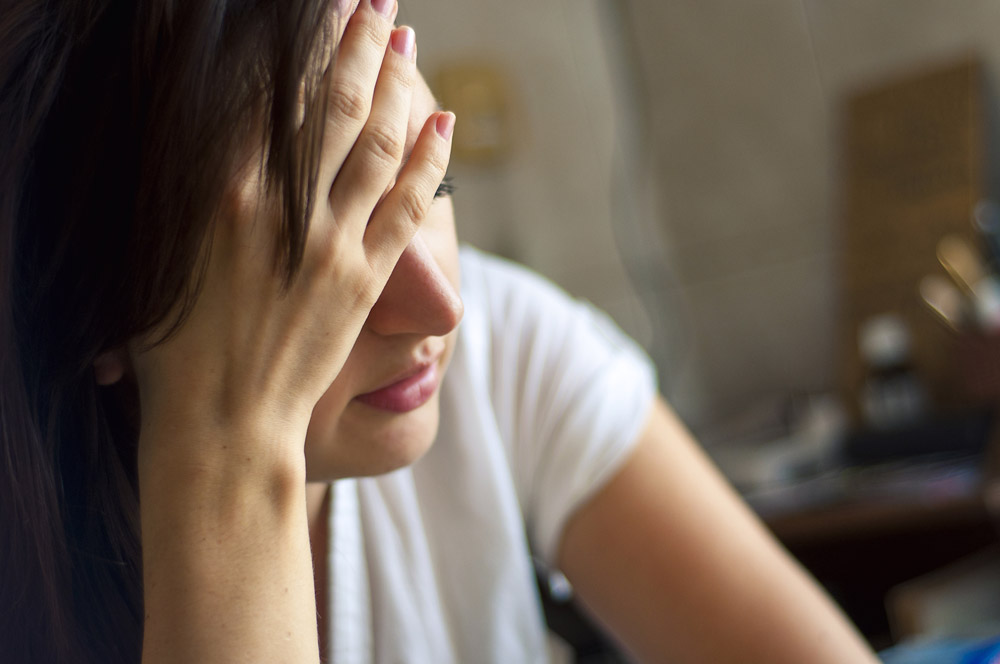

Underrated Migraine Triggers
Migraines have multiple triggers you may not be aware of:
Weather related
Changes in humidity, temperature, pressure, and sunlight exposure are weather-related causes.
Neck pain
Neck pain may also instigate a migraine in some people. Using the wrong pillow and awkward sleeping positions are also related to head pain.
Medical conditions
Even some medical disorders or medications could trigger or worsen your migraines. Despite these known causes, the following unexpected factors may be the reason for your pain.
Bright lights
Photophobia occurs when lights seem too bright, causing head pain. According to experts, these blinding lights trigger the active brain area related to migraines. People experience these issues from car lights at night, snow glare, screens, and even sunlight.
Lighting isn’t the only ocular issue related to head pain, particularly ocular migraines. Studies show that migraine sufferers frequently have dry eye disease. Uncorrected vision problems, eye strain, infections, and eye conditions may also initiate such pain.
Strong smells
Strong smells are another unexpected migraine trigger for some people. In fact, studies show that 78.2% of patients had migraines related to odors. However, not everyone is sensitive to the same scents.
For instance, perfume and tobacco were associated with migraines in 55% and 47% of participants. Other products included fabric softener, body odor, garbage, hair products, and vehicle fumes. Even pleasant smells, such as food, plants, and laundry detergent, may cause migraines.
Loud sounds
Loud noises may contribute to your unpleasant head pain. According to studies, sound hypersensitivity occurs in approximately 70-80% of people with migraines.
Car horns, police and ambulance sirens, crossing bells, and fireworks aren’t surprising migraine triggers. However, some nature sounds, including cicadas, sparrows, or cats, elicited a similar or worse response in some participants.
Sugar in all forms
Small amounts of sugar do minimal damage to the body. Unfortunately, higher levels increase blood glucose levels, which often trigger migraines and headaches. The body lowers high blood sugar by releasing insulin, which also causes migraines.
Sweet treats and beverages are commonly the culprits when dealing with head pain. However, even healthy options could have similar results if you overindulge. It’s best to limit fruit and other natural sweet foods to avoid head pain.
Stress
Those with high-stress jobs or lifestyles are commonly afflicted with migraines. According to experts, daily issues, such as traffic conditions or important work projects, are the worst offenders. These frequent stressors often trigger migraines.
Other strong emotions have similar effects. For instance, those with low emotional intelligence have difficulty handling anger and other powerful emotions. These strong emotional responses, even positive ones, cause migraines in many people.
Resources:
- American Migraine Foundation, June 21, 2023, Weather and Migraine
https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/weather-and-migraine/ - PubMed, Feb. 15, 2022, Prevalence of neck pain in migraine
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35166137/ - National Headache Foundation, Light and Headache Disorders: Understanding Light Triggers and Photophobia
https://headaches.org/light-headache-disorders-understanding-light-triggers-photophobia-2/ - PubMed, Dec. 2012, Dry eyes and migraines: is there really a correlation?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22710496/ - PMC, May 2023, Classification of odors associated with migraine attacks
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10213061/ - PMC, Feb. 1, 2019, Identification of Everyday Sounds Perceive as Noise by Migraine Patients
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6599942/ - Sugar Nutrition Resource Centre, Feb. 28, 2023, Can sugar cause headaches?
https://www.sugarnutritionresource.org/news-articles/can-sugar-cause-headaches - Mayo Clinic, Headaches: Reduce stress to prevent the pain
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tension-headache/in-depth/headaches/art-20046707#:~:text=It’s%20not%20a%20coincidence%20%E2%80%94%20headaches,in%20children%20and%20young%20adults - PMC, Jan. 2022, Migraine Headaches: The Predictive Role of Anger and Emotional Intelligence
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8724728/
This content comprises informative and educational resources only and can not be considered as a substitute for professional health or medical guidance. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk. If you have any inquiries or apprehensions about your medical condition or health goals, talk with a licensed physician or healthcare provider.




Leave A Comment